Understanding Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a medical procedure designed to restore mobility and alleviate pain in individuals suffering from severe hip joint damage. This damage can result from various conditions, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic injury, or avascular necrosis.
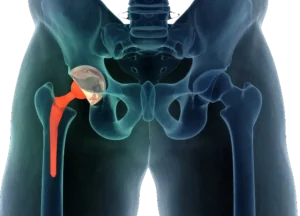
Who Needs Hip Replacement Surgery?
Hip replacement surgery is typically recommended for individuals experiencing significant pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the hip joint, despite conservative treatments such as medication, physical therapy, or assistive devices. Common symptoms that may indicate the need for hip replacement include:
- Persistent hip pain, even at rest
- Difficulty walking or climbing stairs
- Stiffness in the hip joint, limiting range of motion
- Noticeable swelling or inflammation around the hip area
The Procedure: What to Expect
Preparing for Surgery
Before undergoing hip replacement surgery, patients will undergo a comprehensive evaluation by their orthopedic surgeon to ensure they are suitable candidates for the procedure. This evaluation may include medical history assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans.
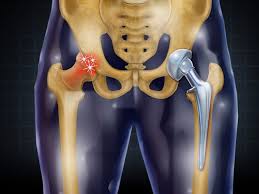
Surgical Technique
During the hip replacement procedure, the damaged parts of the hip joint are removed and replaced with artificial components, known as prostheses, designed to mimic the natural function of the hip joint. The surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia, and may involve different surgical approaches, including:
- Anterior approach
- Posterior approach
- Lateral approach
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Following hip replacement surgery, patients will undergo a period of recovery and rehabilitation to regain strength, mobility, and function in the hip joint. This process may include:
- Pain management strategies
- Physical therapy exercises
- Assistive devices such as walkers or crutches
- Home care instructions provided by healthcare professionals
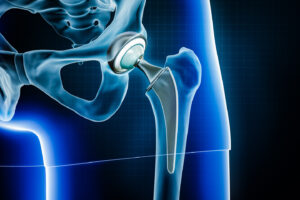
Benefits of Hip Replacement Surgery
Pain Relief: One of the primary benefits of hip replacement surgery is the relief of chronic hip pain, allowing individuals to return to activities they enjoy without discomfort or limitation.
Improved Mobility: By replacing the damaged hip joint with an artificial prosthesis, hip replacement surgery can significantly improve mobility and range of motion, enabling patients to move more freely and engage in daily activities with greater ease.
Enhanced Quality of Life: Hip replacement surgery can have a profound impact on a patient’s overall quality of life, restoring independence, functionality, and well-being.
Risks and Complications: While hip replacement surgery is generally considered safe and effective, it is not without risks. Potential complications may include:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Dislocation of the prosthetic joint
- Nerve or blood vessel damage
It is essential for patients to discuss these risks with their healthcare provider and follow all pre-and post-operative instructions carefully to minimize the likelihood of complications.
While Quadriceps Sparing Knee Replacement offers numerous benefits, it may not be suitable for everyone. Factors such as the severity of knee arthritis, overall health, and lifestyle goals should be carefully considered when determining the most appropriate treatment approach. Consultation with a skilled orthopedic surgeon is essential to assess candidacy for this procedure and discuss individualized treatment options.
Conclusion
Hip replacement surgery is a proven and effective treatment option for individuals suffering from debilitating hip joint conditions. By understanding the procedure, its benefits, and potential risks, patients can make informed decisions about their healthcare and take proactive steps toward improving their quality of life.
If you or a loved one are considering hip replacement surgery, consult with a qualified orthopedic surgeon to discuss your options and determine the most appropriate course of action.
